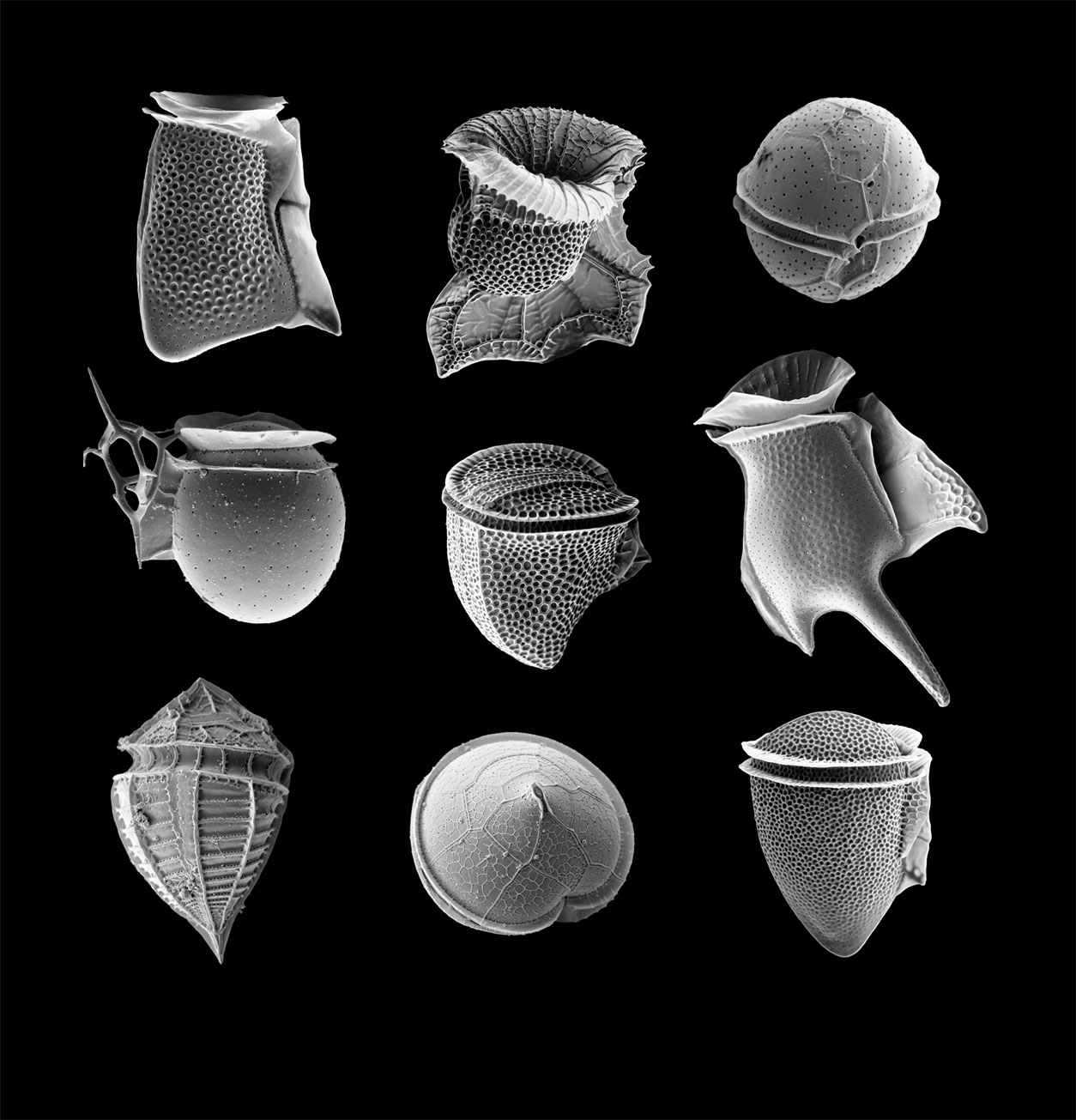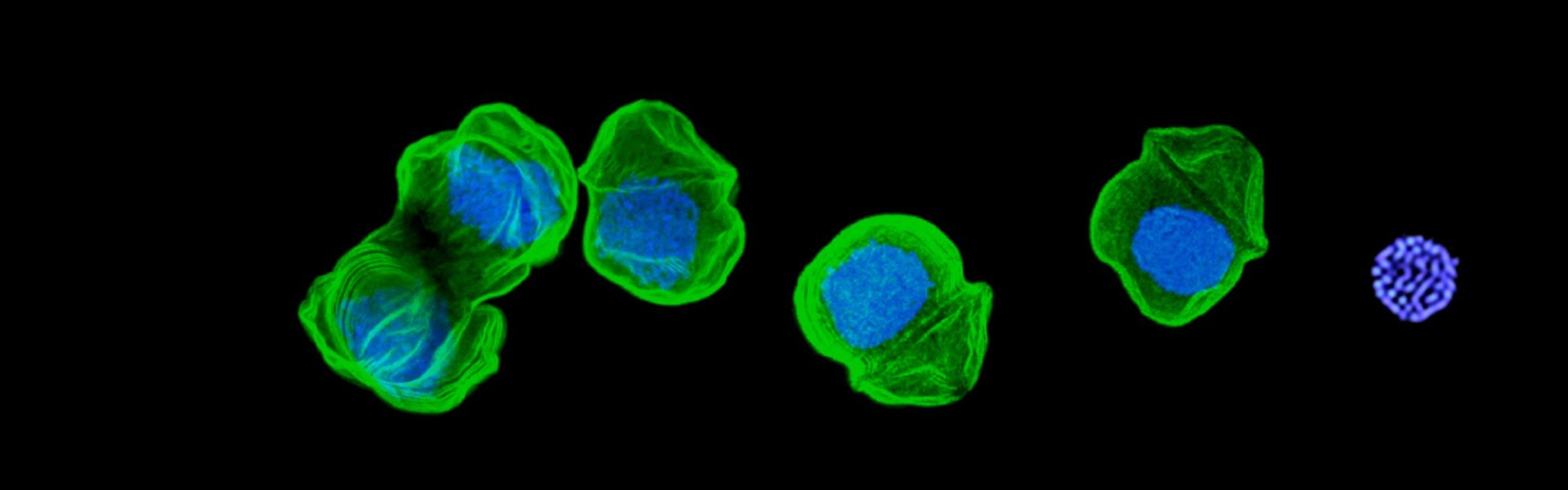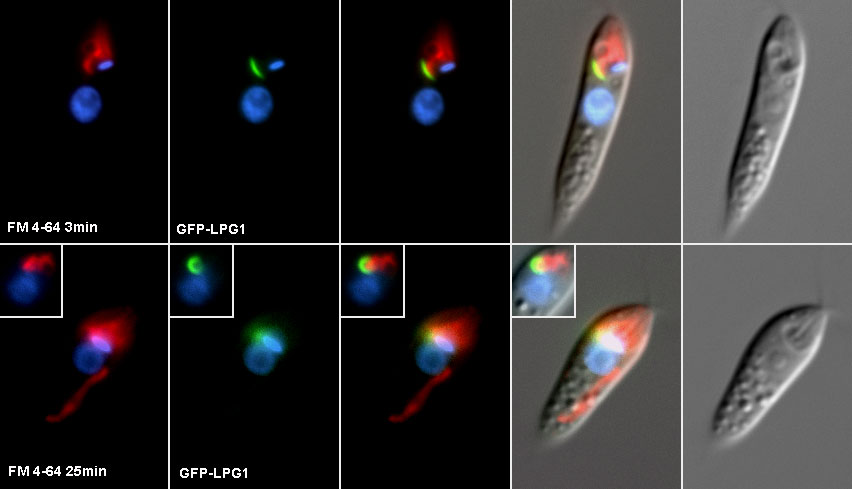
Eukaryotic Diversity
In addition to targeted investigations of key processes in cell function and evolution, the Waller lab has broad interests in exploring and describing diversity in eukaryotes. These have included: describing new taxa; resolving the relationships amongst eukaryotic lineages using molecular phylogenetics; understanding the role of lateral gene transfer in gain and transmission of function; and characterising genetic diversity and evolution through genome and transcriptome sequencing of key groups.
Selected Publications:
- Janouškovec, J. et al (2017) Major transitions in dinoflagellate evolution unveiled by phylotranscriptomics. PNAS 114(2):e171-180
- Woo, Y.H. et al (2015) Chromerid genomes reveal the evolutionary path from photosynthetic algae to obligate intracellular parasites. eLife 4: e06974
- Wetherbee, R. et al (2015) Andersenia, a genus of filamentous, sand-dwelling Pelagophyceae from southeastern Australia. Phycologia 54: 35-48
- Bachvaroff, T.R. et al (2014) Dinoflagellate phylogeny revisited: using ribosomal proteins to resolve deep branching dinoflagellate clades. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 70: 314-22
- Grant, B. et al (2013) Psammomonas australis gen. et sp. nov. (Raphidophyceae), a new dimorphic, sand-dwelling raphidophyte. Phycologia 52(1):57-64
- Grant, B. et al (2011) Platychrysis moestrupii sp.nov. (Prymnesiophyceae): a new dimorphic, sand-dwelling haptophyte species from southeastern Australia. Phycologia 50(6): 608-15
- Kraft, L.G.K et al (2010) Investigations into southern Australian Ulva (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta) taxonomy and molecular phylogeny indicate both cosmopolitanism and endemic cryptic species. J. Phycol. 46(6): 1257-77
- Carpenter, K.J. et al (2008) Surface morphology of Saccinobaculus (Oxymonadida): implications for character evolution and function in oxymonads. Protist 159: 209-21
- Patron, N.J. et al (2007) Origin and distribution of epipolythiodioxopiperazine (ETP) gene clusters in filamentous ascomycetes. BMC Evol. Biol. 7:174
- Eisen, J.A., et al. (2006) Macronuclear genome sequence of the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila, a model eukaryote. PLoS Biology 4:e286
- Waller, R.F. et al (2006) Lateral gene transfer of a multi-gene region from cyanobacteria to dinoflagellates resulting in a novel plastid-targeted fusion protein. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23:1437-43
- Waller, R.F., et al (2006) Phylogenetic history of plastid-targeted proteins in peridinin-containing dinoflagellate Heterocapsa triquestra. Int. J. Sys. Evol. Microbiol. 56: 1439-1447
- Chan, N.C. et al (2006) The C-terminal TPR domain of Tom70 defines a family of mitochondrial protein import receptors found only in animals and fungi. J. Mol. Biol. 358:1010-22
- Dodge M.A. et al (2004) Localization and activity of multi-drug resistance protein 1 in the secretory pathway of Leishmania parasites. Mol. Micro. 51: 1563-75